Methods of Mobile Device Extractions
Extraction of data from a device
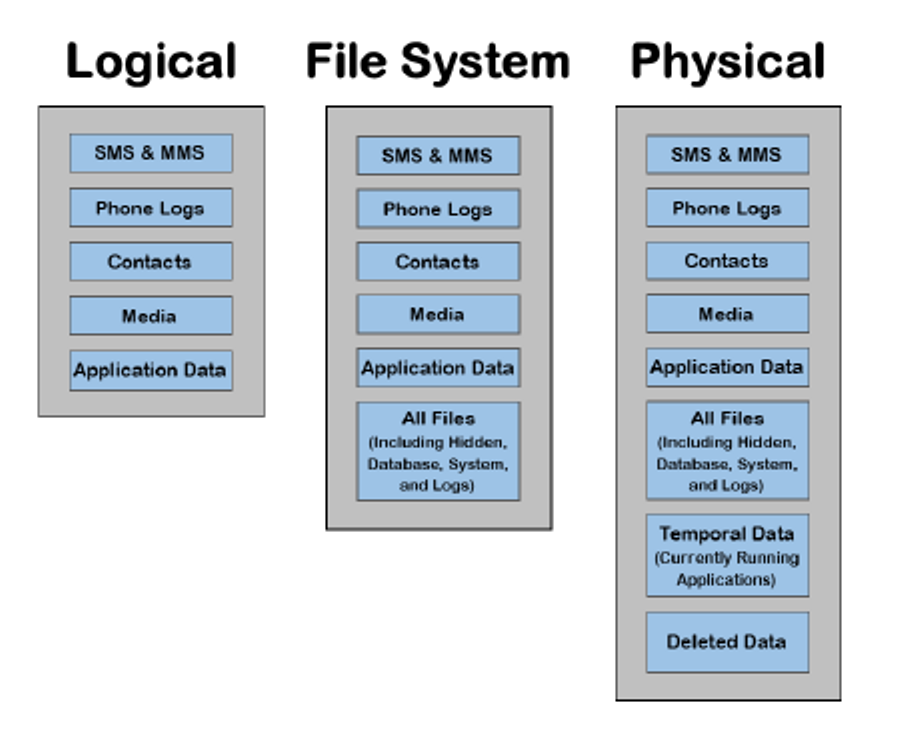
There are three types of extractions that may be performed on a mobile device: logical, filesystem, and physical. The feasibility of these three types of extractions depends upon the make, model and operating system of the mobile device.
What is a Logical Extraction?
Logical Extraction is the quickest and most supported extraction method. In a logical extraction, the forensic tools interact with the operating system of the mobile device using an API (Application Programming Interface). This API (Application Programming Interface) is tool that interacts with the software of the mobile. There are two kinds of the Softwares in a mobile. The first one is the base Software called its OS. Second class of Softwares are installed to work as per the commands of the base Software i.e., the OS. These second class Softwares are the applications or Apps. And the API (Application Programming Interface) communicates with both the Softwares i.e., the OS and the Apps.
The extractor can extract most of the live data on the device e.g. SMSs (Short Messaging Service, commonly known as text messages), call logs, MMS(Multimedia Messaging Service, which are generally text messages with attachments or group text messages), Apps without password etc. The extracted data is output into a readable format.
There is one interesting aspect of the Logical Extraction. Individual items cannot be extracted, the whole class will be extracted. For example one can choose to extract SMS data, but all SMS will be collected not just conversations between specific people or phone numbers.
In Logical Extraction only the live data i.e. the data available in the device will be extracted. Any password protected data or deleted data will not be available to the Logical Extraction.
What is a Filesystem Extraction?
The filesystem extraction is more data extracting method if compared to the Logical Extraction. In Logical Extraction the data of a device was extracted with an an API (Application Programming Interface) and hence only that much data could be extracted which was within the reach of that API.
In File System Extraction the data of the device is not approached through an API and hence, the limitations of the API is not a bar here. On the other hand the data is approached through the Forensic Tools used by the extractor. Now the extractor can reach deeper levels of data.
In the File System Extraction the access to the data inside a device is direct and without any API hence the Forensic Tools can extract all files present in the internal memory including the database files, system files and logs. File System Extraction can examine the file structure, the web browsing including history and downloads and logins, usage of Apps, their history and chats etc.
The most important part of a File System Extraction is the full access to the database files on a mobile device. Numerous applications, such as iMessage, SMS, MMS, Calendar and others, store their information in database files. When a user deletes data that is part of a database, such as SMS, the entry within this database is marked as deleted and is no longer visible to the user. This deleted data remains intact within the database and is recoverable until the database performs routine maintenance and is cleaned up. Once this process occurs the data is no longer recoverable.
What is a Physical Extraction?
The Physical Extraction is the most inclusive kind of extraction. This is the most extensive but least supported extraction method. Physical extraction is least supported because getting full access to the internal memory of a mobile device is completely dependent upon the operating system and security measures employed by the manufacturer like Apple and Samsung.
The OS of Samsung phones is based on an open source system called Android. It gives more access to the Forensic Tools. But there are some other OS e.g. iOS, Symbian, BlackBerry, Kai OS, Windows Mobile, Sailfish etc. which are not open source OS. Even the latest Forensic Tools like Cellebrite cannot penetrate them. All iOS 7 onwards are difficult to access the complete Physical Extraction of the device. Now iOS 11 onwards are completely extraction proof OS.
A physical extraction from a mobile device shares the same basic concept as the physical forensic imaging of a computer hard drive. A physical extraction performs a bit-by-bit copy of the entire contents of the memory of a device. This extraction allows for the collection of all live data and also data that has been deleted or is hidden.
By having a bit-by-bit copy, deleted data can be potentially recovered .This means that data that resides outside of the active user data and database files, such as: images, videos, installed applications, location information, emails, and more are able to be extracted and deleted versions of these items may be recovered as well.
Methodology used by Forensic Experts
The Forensic Experts use different kinds of techniques to reach the innermost data of your Mobile Phone. In Logical Extraction they use API (Application Programming Interface) and in the remaining two extractions i.e. the File System Extraction and the Physical Extraction they bypass the OS of the device. This is done at a stage just before the OS of device starts to set in. The stage is called BOOTLOADER.
Bootloader
The Bootloader is the first thing that starts up when a device is turned on. At its most basic level, a Bootloader is the low-level software on your device that allows the next Software on your device i.e. OS to run. Without a Bootloader your OS will not run and you will not be able to see the Graphic User Interface (GUI) on your mobile.
Forensic Tools
The Forensic Experts use their Forensic Tools to disturb the working of Bootloader. In the normal course of working a Bootloader prompts the OS to start. But the Forensic Tools used would give a command to the Bootloader not to prompt the OS of the device rather they force their own different OS to start and fetch the data available in device.
Data Extraction
Here, onwards everything depends upon the comparative penetrating power of the tools employed by the Forensic Experts and the structure in which the data of the device is kept in the internal memory i.e. the file structure.
Even the latest tools are unable to fetch data from some closed source of OS e.g. iOS, Symbian, BlackBerry.
Forensic Tools for Mobile Phone
Oxygen Forensic Detective
Oxygen Forensic Detective is capable of extracting data from a number of different platforms, including mobile, IoT, cloud services, drones, media cards, backups and desktop platforms.
It uses physical methods to bypass device security (such as screen lock) and collects authentication data for a number of different mobile applications. Oxygen is a commercial product distributed as a USB dongle.
Cellebrite UFED
Cellebrite offers a number of commercial digital forensics tools, but its Cellebrite UFED claims to be the industry standard for accessing digital data. The main UFED offering focuses on mobile devices, but the general UFED product line targets a range of devices, including drones, SIM and SD cards, GPS, cloud and more. The UFED platform claims to use exclusive methods to maximize data extraction from mobile devices.
XRY
XRY is a collection of different commercial tools for mobile device forensics. XRY Logical is a suite of tools designed to interface with the mobile device operating system and extract the desired data. XRY Physical, on the other hand, uses physical recovery techniques to bypass the operating system, enabling analysis of locked devices.
CAINE
CAINE (Computer Aided Investigative Environment) is the Linux distro created for digital forensics. It offers an environment to integrate existing software tools as software modules in a user-friendly manner. This tool is open-source.
SANS SIFT
SIFT is another open-source Linux virtual machine that aggregates free digital forensics tools. This platform was developed by the SANS Institute and its use is taught in a number of their courses.
SANS SIFT
SIFT is another open-source Linux virtual machine that aggregates free digital forensics tools. This platform was developed by the SANS Institute and its use is taught in a number of their courses.
HELIX3
HELIX3 is a live CD-based digital forensic suite created to be used in incident response. It comes with many open-source digital forensics tools, including hex editors, data carving and password-cracking tools. If you want the free version, you can go for HELIX3 2009 R 1. After this release, this project was taken over by a commercial vendor. So, you need to pay for the most recent version of the tool.
This tool can collect data from physical memory, network connections, user accounts, executing processes and services, scheduled jobs, Windows Registry, chat logs, screen captures, SAM files, applications, drivers, environment variables and internet history. Then it analyzes and reviews the data to generate the compiled results based on reports.
A complete encyclopedia about the CDR the Wonder-Word has been given.