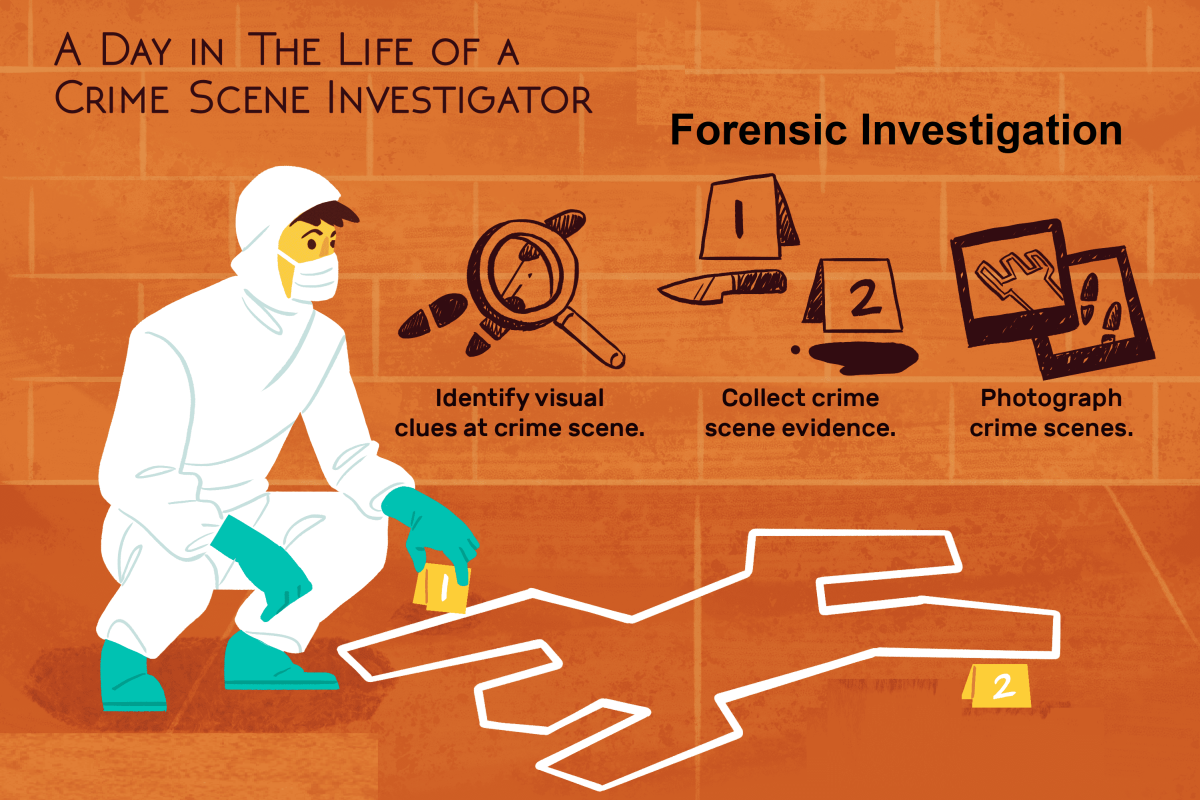
Forensics in the Courts
People can lie but the material evidence does not.
Forensics have helped us to read and understand the material evidence in depth.
In the year 2019 there was case the high ranking officials of FSL Rohini were suspected to be involved in manipulating the samples of the accused persons, which were sent to them for examination and detection. The Delhi High Court directed the CBI to register a Criminal Case against them. The aforesaid senior officials are now facing a trial in the Court where a Charge Sheet was filed against them.
Detection of body fluid is one area where the forensics or the forensic science has come to help the Courts.
Chuck Palahniuk a Fiction Writer, once writes:
“Everything is a self-portrait. A diary. Your whole drug history’s in a strand of your hair. Your fingernails. The forensic details. The lining of your stomach is a document. The calluses on your hand tell all your secrets. Your teeth give you away. Your accent. The wrinkles around your mouth and eyes. Everything you do shows your hand.”
and the same thing can be said with confidence about the forensic science.
The forensic science, has grown a multifaceted structure to help the Courts. And the good thing is that it has not stopped. It is still growing and developing new areas where it can assist the Courts. Presently, the main areas of help where the forensics do assist a Court are given here:
1. Trace Evidence Analysis:
The question is whether a particular aspect of occurrence of a crime would furnish information about the occurrence of the crime. For this purpose the forensics use the basic fault-lines of the crimes – every contact creates an impression and can be recovered forensically.
Everything that had happened during the occurrence of a crime is recovered is recovered by the forensics and presented before the Courts by an expert of the forensics. Trace evidence covers a large area. It may contain anything e.g. a human/animal hair, rope, soil, fabric fibers, feathers, building materials etc. Trace Evidence Analysis effects the recovery of such evidence and their forensics conducts examination to obtain information that can be used in the court of law.
2. Forensic Toxicology:
There may be toxic substances inside a human body with a historical back up in viscera, hair or nails of that body. The forensics gathers and studies such toxic substances. Various Toxins might be susceptible to different techniques but still they are made recoverable and analyzable by the forensic experts.
Forensic Toxicology undertakes methods and procedures from various other disciplines such as lab technologies, analysis, clinical chemistry, and pharmacology etc. to ascertain the death of the deceased. Forensic Toxicology is very helpful in road accidents, poisoning, and sexual violence.
3. Forensic Psychology:
Every suspect has a personality and a psychology. Sometimes there are perpetrators who hate a race, a gender or a particular type of worker. Their all criminal actions are oriented against such groups of gender, race, age or workers.
Forensic Psychology assists the study of personal traits and behavioral patterns of such criminals. Forensic Psychologists prepare a psychological portrait or criminal profiles of the criminal and anticipate what he is going to do the next. Forensic psychologists even help counselling of the victims and evaluating the custody issues of a child when the parents are in dispute. they also provide various anticipated information about the commission and/or the repetition of the crime.
4. Forensic Podiatry:
Various people have specific history of their lower limbs, trauma incidents, anatomy and musculoskeletal functions of their legs and feet. These bodily histories of the perpetrators may become relevant as evidence while investigating or appreciating the method of perpetration of crime.
This is particularly helpful in the investigation of foot-based evidence with respect to a criminal incident.
5. Forensic Pathology:
This forensic pathology determines how the death of a corpse had occurred. It studies various body functions particularly of air passages, alimentary canal and liquid intakes to ascertain the cause of death and the time of death.
For example, a forensic pathologist can examine a wound to identify the weapon used to cause that wound. Hence, forensic pathology extracts and analyzed the evidences from a corpse to determine whether the death is natural, criminal or accidental.
6. Forensic Odontology:
Odontology is the study of denture, teeth and other related aspects.
Forensic Odontology [or sometimes it may be called Forensic Dentistry] is the science of proper handling, analysis, and evaluation of any form of dental evidence of the deceased. These odonatological evidence must be legally admissible evidence in a court of law. When the victim’s body is found in an unrecognizable state, the forensic odontology helps investigators in identifying them and presenting to the Courts.
Forensic dentists studies and prepare a profile of the denture of the deceased in a traceable and verifiable manner. Such a profile may include the medicines taken, the filling in the teeth, previous RCTs etc. and even wired restructuring of the jaws.
Criminal investigations comprising bite marks yield an abundant data to the Forensic Odontology.
7. Forensic Linguistics:
Forensic Linguistics undertakes the study of written and/or spoken language of the perpetrator and the victim both. Forensic Linguistics provides an abundant data about the age, gender, education, ethnic and cultural information, socio-economic level and geographical background of the perpetrator and the victim both.
Forensic Linguistics provides immense help in relation to emergency calls, demands of ransom, suicide notes, threatening calls or social media messages by anyone of the perpetrator and the victim both.
8. Forensic Geology:
In several cases the evidence on the spot of crime is in the form of Earth, oil, petroleum, ores, minerals, metallurgical reactants, soil, rocks and other similar substances. These type of evidences contain an abundant data about the Geological Location or Information of the incident.
Forensic Geology or Geoforensics examine those recovered materials and compares and studies them with the Geological Information available. Such a study would reveal information about the location, date, time, area and the nature of the incident related to the perpetrator and the victim both.
9. Forensic Entomology:
Forensic Entomology is the study of insects and other arthropods e.g. arachnids, centipedes, millipedes, and crustaceans. When such an information is available on the spot of the crime, Forensic Entomology comes forward to study the same. It also gives chronological details relating to death investigation, determination of the location of an incident, postmortem interval and to arrive at the precise time of the infliction of wounds.
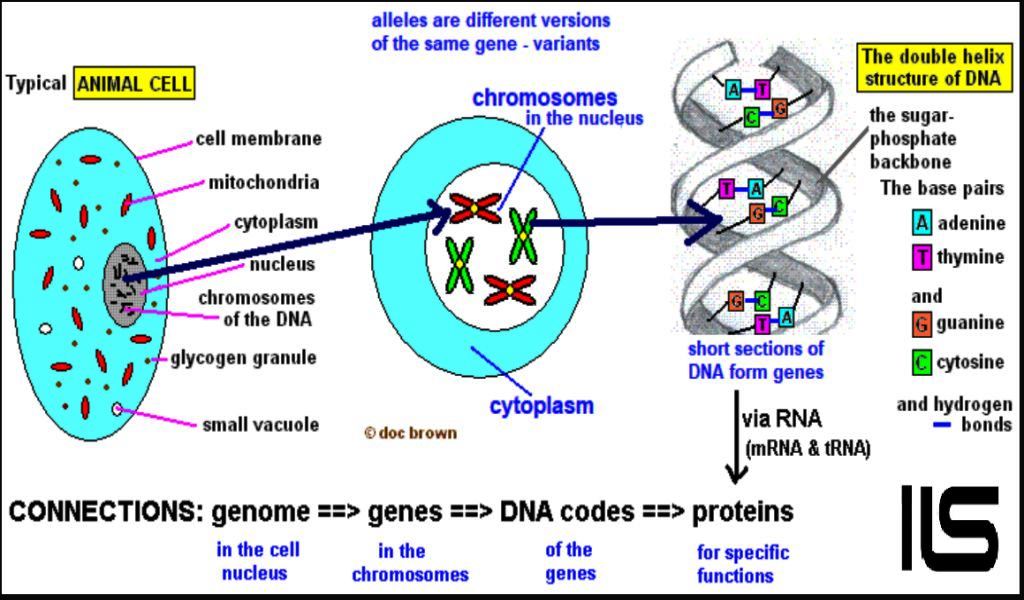
10. Forensic DNA Analysis:
When the body fluids are found on the Spot of Occurrence their DNA fingerprinting is prepared. 16 specific DNA markers are compared in India. In the US they used to study 13 markers but 2017 onwards they have adopted a system of 20 DNA Markers. Through this DNA Fingerprinting the sought out person can be zeroed down precisely.
The biological evidence used for DNA profiling are hair, skin, semen, urine, blood, saliva and even body remains in burn cases.
11. Forensic Archeology:
Wonder how geophysical and geological surveying techniques are used in forensics? That’s Forensic Archeology for you! Such techniques along with the use of photography and imaging enable forensic archeologists to assist the police and investigating officers to identify the site where the victim’s body and personal items, or robbed goods are buried. Forensic archeologists are also often leveraged for carrying out excavations or digs at historical and pre-historical sites. Such scientists are adept at using a range of techniques, one being carbon dating, to ascertain the age of items retrieved during an excavation. They often carry out mass excavations to produce evidence for war crimes trials, gas or bomb explosions, plane crashes and the like.
12. Forensic Anthropology:
Sometimes only bones, fragments of bones or skin, singed hair, burnt nails etc. are available from Spot of Occurrence. A Forensic Anthropologist comes and studies the remnants traceable after the alleged mutilation, burning, natural degradation etc. Forensic anthropologists can examine human bodies/skeletons to help identify the individuals and arrive at the cause of death. From the remnants the age, sex, race and physique of the sought after person can be determined. they can also determine the manner of death (suicide, accidental or due to disease), as well as if a bone injury retrieved was before, during or after the death.
13. Digital Forensics:
Sometimes the available evidence is in the form of digital evidence. This may be available from computers, hard drives, Flash drives and USB sticks. There are various forensic tools to retrieve the lost data from such digital sources. These Digital pieces of data may be used or found available to have been transmitted over the internet to commit a cybercrime.
Digital Forensics is to gather and analyze such a digital data so that it can be produced in a Court of law as an admissible piece of evidence.
14. MOBILE FORENSICS
These days mobile phones have combined the Digital Data with the Internet and that too over a volatile memory. The Rules of Game are different for Mobile Forensics as Compared to the Digital Forensics used for computers or the Cyber Rules used for web based activities. The Mobile Forensics have merged them all on one hand and had also acquired the status of the most used platform for storing such an information.
15. Forensic Ballistics:
Forensic Ballistics extracts and analyze the information about the use of any evidence related to firearms (bullets, bullet marks, shell casings, gunpowder residue etc.).
The cases where the firearms were suspected to have been used the investigation is undertaken by a Forensic Ballistic Expert to draw inferences on the exact weapon used, the distance, velocity, and angle of firing, and ultimately the shooter himself.
When you are dragged in a Court Case not because of your fault but because someone is allowed to misuse a law.
Victim of a Bad Judgment: When you are indicted not by a Judgment but by the poor quality of Judgment delivered.
Chamber No. 103, 104
AGGARWAL CHAMBERS
CD Block Pitampura
Delhi 110034
Call
+91 9910765379
When you are indicted not by a Judgment but by the poor quality of the Judgment. Judge’s ignorance also contributes.
With the growing demand for examination of cellular phones a need has also developed for the guidelines of process.
Serological Experts misuse the Court System because Defence Counsel, Prosecutors and the Judges are ignorant.
It is has been proved by Israeli Scientists that fabricated DNA can be prepared and used wherever required.
The question is whether just the presence of matching DNA significant (regardless of whether it came from semen, cells or another body fluid).
Were there ‘legitimate’ opportunities for a DNA transfer
People are equally aggrieved by the Bad Convictions. The best remedy against a Bad Conviction is to challenge it before a superior Court in Appeal / Revision.
The Advocate decides it.
This is a step by step explanation for understanding STRs in DNA fingerprinting. Even a Layman can understand the technical terminology used in those Reports.
Better to read it.
You are made Victim of False Allegation consequent to a greed, revenge, retribution or for trapping you so that your adversary attains another goal. They misuse the Law. And Someone pays for the whole life.